Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term glucose metabolic disorder with substantial clinical effects. Microvascular (retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy) and macrovascular (ischaemic heart disease, stroke, peripheral vascular disease) consequences are among the multi-system problems of diabetes.
The pancreas secretes insulin and serves as a vital player in glucose absorption. Insulin draws glucose from the food we ingest, and glucose subsequently enters the circulation. The cell finally takes glucose to produce energy.
In the blood, all carbohydrate foods are broken down into glucose. Insulin facilitates the entry of glucose into cells.

Inability to produce or use insulin effectively results in elevated blood glucose levels, known as hyperglycemia. Glucose remains in the circulation and does not enter the cells. Glucose buildup in the blood creates medical concerns over time.
This illness is sometimes referred to as “a touch of sugar” or “borderline diabetes.” These phrases appear to be innocuous, yet every occurrence of this disease is serious..
Diabetes is the most prevalent disease in the world. IDF Diabetes Atlas Ninth edition 2019 gave us a fact & figure:
- Approximately 463 million adults were living with diabetes;
- By 2045 this number will hike to 700 million.
- 1 out of 5 people who are above 65 years old has diabetes.
- Undiagnosed- 1 out of 2 (232 million) people with diabetes
- 4.2 million deaths due to diabetes
- children and adolescents- More than 1.1 million are living with type 1 diabetes
Types of Diabetes

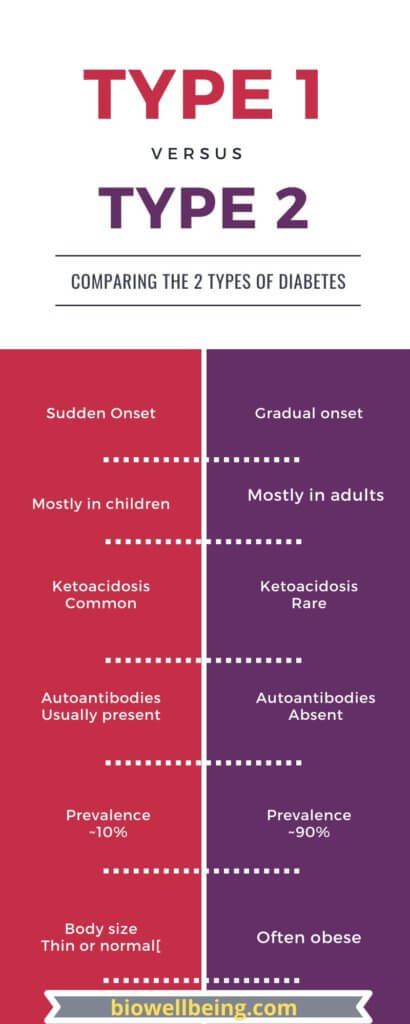
There are three major types of diabetes – Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational.
Type 1 diabetes is more common in children and teenagers, but it can occur at any age.
Type 2 diabetes is more frequent in adults, accounting for almost 90% of all cases. When a person develops type 2 diabetes, his or her body is unable to properly use the insulin produced by the body. People with type 2 diabetes will need to take oral medications and/or insulin to keep their blood glucose levels under control.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is often referred to as juvenile diabetes. Type 1 affects around 10% of the population. It can afflict people of any age, although it most commonly affects children and young adults.
Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune reaction (when the body sends antibodies and immune cells to target the body’s own healthy tissues by mistake). As a result, your body’s defence attacks the insulin-producing cells. The consequence is, little or no insulin is produced. The specific reasons are unknown, although they are thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Type 1 diabetes requires daily insulin injections to keep blood glucose levels under control. People with type 1 diabetes may increase the chance of fatality if they do not have access to insulin. Hence, they are often recommended to check their blood glucose levels at least four times each day.
Symptoms of Type 1
The most common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
- Abnormal thirst and dry mouth
- Sudden weight loss
- Frequent urination
- Lack of energy, tiredness
- Constant hunger
- Blurred vision
- Bed-wetting
Diagnosis Of Type 1
Diagnosing type 1 can be difficult so additional tests may be required to confirm a diagnosis.
Health care professionals usually test people for type 1 if they have clear-cut symptoms of this disease.
Health care professionals frequently use the random plasma glucose (RPG) test to diagnose type 1. This blood test measures out your blood glucose level at a single point in time.
Sometimes health professionals use the A1C blood test as well, to find out how long someone has had high blood glucose.
To find out if you have type 1, your health care professional may test your blood for certain auto-antibodies.
Auto-antibodies are antibodies that attack healthy tissues and cells by mistake. The presence of certain types of auto-antibodies is common in type 1 but not in type 2.
Because type 1 can run in families, your health care professional can test your family members for auto-antibodies. Type 1 Trial Net, an international research network, also offers auto-antibody testing to family members External link of people diagnosed with the disease.
The presence of auto-antibodies, even without any symptoms, means the family member is more likely to develop type 1.
If you have a brother or sister, child, or parent with type 1, you may want to get an auto-antibody test.
People age 20 or younger who have a cousin, aunt, uncle, niece, nephew, grandparent, or half-sibling with type 1 also may want to get tested.
What Are the Treatments of Type 1?
All people with type 1 need to take insulin to control their blood glucose levels. We can categorize different types of insulin depending on how quickly they work when they peak, and how long they last. Insulin is commonly delivered with a syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump.
Different types of insulin, what are the plans normally used are described in the below sections.
How to Prevent Type 1?
No effective and safe intervention currently exists to prevent type 1 despite a large number of clinical trials aimed at halting the on-going autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells.
However, there is some evidence that overweight and a high growth rate in children are weak risk factors, indicating that a healthy lifestyle that avoids both over-eating and a sedentary lifestyle is recommended for high-risk groups such as the siblings of children with type 1.
Nevertheless, this is just one of several factors that have also been implicated. These include not being breast-fed, being the first-born, being born by Caesarean section (also called C-section), and having an older or obese mother.
Although a ‘cure’ for type 1 is being actively sought, preventing or delaying it in those known to be at risk or, in those already diagnosed, slowing down the auto-immune destruction of beta cells and protecting those cells that are still active are likely to be more achievable goals in the foreseeable future.
Health Problems With Type 1 Development:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Eye problems
- Dental disease
- Nerve damage
- Foot problems
- Depression
- Sleep apnoea (temporary halting of breathing, especially during sleep)
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 is the most common type, accounting for around 90% of all diabetes cases.
We generally defined this as insulin resistance, where the body does not fully react to insulin.
Because insulin cannot work in good order blood glucose levels keep increasing, releasing more insulin.
For some people with type 2, this can sooner or later tire the pancreas, resulting in the body producing less and less insulin. This will cause even higher blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
It is most commonly diagnosed in older adults but is increasingly seen in children, adolescents, and younger adults due to rising levels of obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet.
What Are the Risk Factors of Type 2?
Several risk factors have been associated with type 2 and include:
- Family history of any
- Overweight
- Unhealthy diet
- Physical inactivity
- Increasing age
- High blood pressure
- Ethnicity
- Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)- (a category of higher than normal blood glucose, but below the threshold for diagnosing type 1&2)
- History of gestational
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy
What Are the Symptoms of Type 2?
The symptoms of type 2 are similar to those of type 1 and include:
- Excessive thirst and dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Lack of energy, tiredness
- Slow-healing wounds
- Recurrent infections in the skin
- Blurred vision
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet.
What Are the Diagnostic Test for Type 2 Diabetes?
These symptoms can be mild or absent and so people with type 2 may live several years with the condition before being diagnosed.
Tests Performed:
Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test: This blood test will show your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months.
- Normal levels – below 5.7 percent
- Prediabetes: result between 5.7 and 6.4 percent is considered.
An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests means you have type 2.
If the A1C test isn’t available, or if you have certain conditions — such as an uncommon form of hemoglobin (known as a hemoglobin variant) — that interfere with an A1C test, your doctor may use other tests to diagnose:
Random blood sugar test: This test doesn’t consider you meal when you last ate. If a blood sample showing the blood sugar level is 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests diabetes.
With this, if you have signs and symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination and intense thirst, it will suggest diabetes.
Units of this test -milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
Fasting blood sugar test: This test take your meal into consideration. After an overnight fast, your blood sample will be taken.
- Normal: A reading of less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L)
- Prediabetics: A level from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L)
- Diabetes: If your fasting blood sugar is 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests
Oral glucose tolerance test: infrequently used than the others. But during pregnancy this test is favorable.
In this test also meal is taken into consideration. You’ll fast overnight and then drink a sugary liquid at the doctor’s office.
Periodically the Blood sugar levels are tested for the next two hours.
- Normal: A blood sugar level of less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L)
- Prediabetics: between 140 and 199 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L and 11.0 mmol/L)
- Diabetes: A reading of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher after two hours
What Are the Treatments of Type 2?
- Weight loss: Try to lose weight if you are heavy. Losing 5-7% of you current weight will help you to delay diabetes and other health problems. For example, if you weigh 200 pounds, your destination would be to lose about 10 to 14 pounds.
- Physical exercise: Get at least 30 minutes of physical activity, such as walking, at least 5 days a week. Start slowly and build up to your goal. Ask your doctor which physical exercise is best for you.
- Balance and Healthy diet: Eat healthy foods. Eat smaller portions to reduce the number of calories you eat each day and help you lose weight. Opting for foods with less fat is another way to cut calories. Drink water instead of sweetened beverages.
- Blood sugar monitoring: Monitor your blood sugar daily and whether your sugar level is on track or increased. If increased then try to do more exercise and eat organic.
- Medication and insulin therapy: If your sugar level is not coming on track even after exercise and proper diet then you need some medication and insulin therapy.
These steps will help maintain your blood sugar level near normal, which can hold up or prevent complications.
How to Prevent Type 2?
Several factors influence the development of type 2 diabetes. The most powerful are lifestyle behaviors commonly associated with urbanization.
Research indicates that a majority of cases, up to 80% according to some studies, of type 2 diabetes could be prevented through a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
- Healthy Diet: A healthy diet includes reducing the number of calories if you are overweight,
- Replace saturated fats (eg. cream, cheese, butter) with unsaturated fats (eg. avocado, nuts, olive, and vegetable oils),
- Eat dietary fiber (eg. vegetables, fruit, whole grains),
- Avoid tobacco use,
- Avoid excessive alcohol and added sugar.
- Regular physical activity is necessary to maintain blood glucose levels under control. It is most effective when it includes a combination of both aerobic exercise and resistance training. Aerobic exercise includes eg. jogging, cycling, swimming, etc. The inactive time you spent should be the minimum.
- Yoga can be very beneficial for a diabetic. Some specific yogas are there that can help you to control your diabetes.
In a healthy diet, some most common quires are can a diabetic eat watermelon, guava, oat, and apple cider vinegar? These foods are more regular in daily life.
Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes (GDM) is a type of that belong to high blood glucose during pregnancy and is connected with complications to both mother and child.
GDM usually disappears after pregnancy but women are affected and their children are at increased risk of developing type 2 later in life.
What Are the Risk Factors and Precautions for Gestational Diabetes?
- Age: If a woman is older than age 25 are at increased risk.
- Family or personal history: If you have prediabetes, your risk of diabetes increases. Prediabetics is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. If a close family member, can be your parent or sibling, has type 2 diabetes you also have risk of this diabetes.
You’re also at greater risk if you had gestational diabetes during a preceding pregnancy, if you delivered a very large baby or if you had an unexplained stillbirth.
- Weight. Being fat before pregnancy increases your risk.
- Race. These reasons aren’t clear. Women who are black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Asian are more probable to develop gestational diabetes.
Symptoms & Treatments of Diabetes
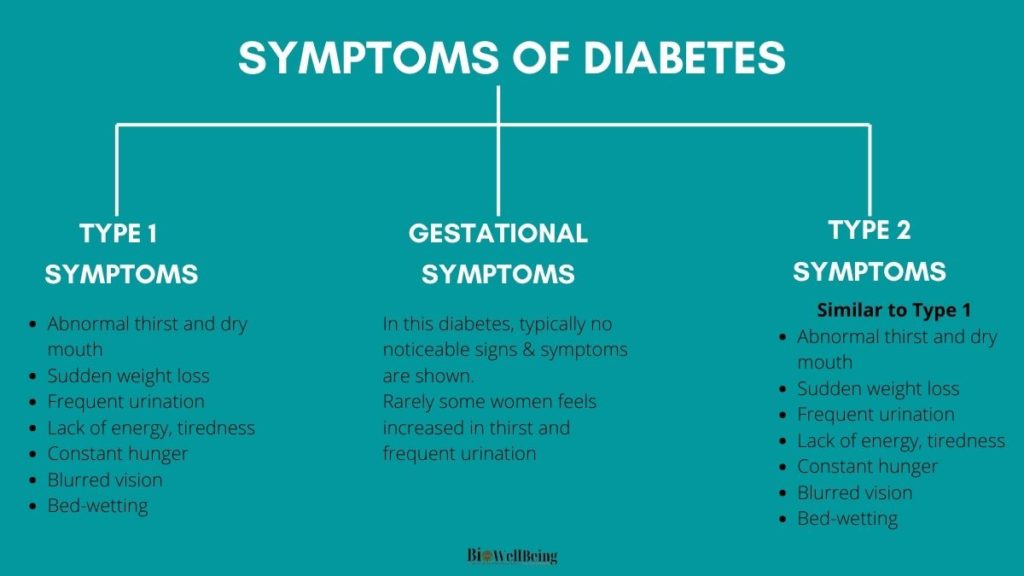
As we know diabetes is categorized into three different types. We don’t actually see any symptoms or treatment for particularly, rather we see about the symptoms and treatments of type 1 or type 2.
Because when we say someone has diabetes then it means that he is suffering from type 1 or type 2 or gestational. So, to know about the symptoms and treatments and test, refer above sections under type 1 and type2.
Types of Insulin In Diabetes Treatment:
Rapid-acting:
These are usually taken just before or with a meal. These insulin act very quickly to limit the rise in blood sugar, which follows eating.
It is essential to avoid over-dosage to minimize the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Rapid-acting insulin includes Asparat, Glulisine, Lispro.
Short-acting:
Usually taken before meals. These insulin are also called regular or neutral insulin.
They do not act as quickly as rapid-acting insulin and therefore may be more appropriate in certain people.
Short-acting insulin includes Actrapid, Humulin R, Insuman Rapid.
Intermediate-acting:
These are often taken together with short-acting insulin. Intermediate-acting insulin starts to work within the first hour of injecting, followed by a period of peak activity lasting up to 7 hours.
Intermediate-acting insulin includes Humulin NPH, Protaphane, Insulatard.
Long-acting:
The insulin that is steadily released and can last in the body for up to 24 hours. They are commonly taken in the morning or the evening, before going to bed.
Long-acting insulin includes Detemir, Glargine.
Common Insulin Treatment Plans Includes:

Twice-daily insulin: By using both Short-acting and Intermediate-acting insulin.
Self-monitoring: People with diabetes who need insulin must check their blood glucose levels regularly to inform insulin dosage.
The process of blood glucose testing by the people with diabetes at home, school, work, or elsewhere is named as Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SBMG).
SMBG helps people with diabetes and their health-care providers understand how their blood glucose levels vary during the day so that their treatment can be adjusted accordingly
Diabetes Info-graphics:

References:
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20371444
- https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes.html?gclid=EAIaIQobChMIg6yivKDl5wIVGh4rCh3TKQw_EAAYASAAEgIckfD_BwE
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323627#types
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes
- https://www.idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-figures.html

[…] insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Maintaining a healthy diet is vital for treating diabetes, and one of the most important components of a balanced diet is choosing the appropriate type of […]
[…] sugar. Based on previous studies, it has been projected that persons with glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes who consume chilli will improve their blood glucose levels. It also aids in the normal generation […]
[…] healthy gut flora has been linked to fewer infections, less inflammation, and a lower risk of diabetes, according to research. The strongest antioxidant present in sweet potatoes is beta-carotene. It is […]
[…] to the CDC, Diabetes is among the 7 leading causes of death in the US. What is more, the number of people aged 65+ grows […]
[…] and can be consumed in many forms. They are low on fat and sodium and can be eaten by people with diabetes to the ones with heart problems, and high blood pressure, from kids to the elderly, everyone can […]
[…] People who eat diets that include vegetables and fruits are at minimal risk of developing cancer, heart disease, inflammation, and diabetes. […]
[…] like ginger, are indicated for certain conditions and are not recommended for others, such as type 2 diabetes, pancreatitis, liver or kidney disease, pre-existing heart problems, and ulcerative […]
[…] shrimp can be considered healthy for people with diabetes only if you cook them […]
[…] diabetes can mimic signs of low testosterone levels. Now, you have heard about possible cardiovascular […]
[…] Read More: Diabetes: Type 1 & 2, Gestational, Causes, Treatments, Insulin, Symptoms […]
[…] matter as such. You need to lose fat and reach a healthy body weight so that you can easily avoid diabetes, heart diseases, liver diseases, and high cholesterol level. Study shows that men who are obese […]
[…] is a health problem that affects all children as well as adults. There are numerous reasons for diabetes to occur like hereditary and an unhealthy lifestyle. Our upper neck and middle of the back help aid […]
[…] Sweet corn is rich in fiber and proteins and also low in fat and sodium content. Sweet Corn For Diabetes is a limiting food. What will be the consequences If a diabetic eat sweet corn? In this article, we’ll discuss the consumption of sweet corn concerning diabetes. […]
[…] for at least 5 days a week can reduce the chance of getting diabetes by up to 30%, especially Type 2 […]
[…] Let’s find out, “Is muskmelon good for diabetes?” […]
[…] you have diabetes, it’s normal to avoid candies since these contain high levels of glucose. But, there are […]
[…] persons with medical conditions like diabetes mellitus and mouth breathing habits are easy […]
[…] Diabetes is a disease that commonly causes high blood sugar. Diabetes is one of the most common conditions suffered among the entire population worldwide. […]
[…] Fruit may earn an excellent addition to a nutritious diet, but also much fruit, or swallowing many fruits high in sugar could be problematic for people who have Type 2 diabetes. […]
[…] with fiber, beneficial for weight loss and diabetes […]
[…] studies are going on but didn’t come to any conclusion about the use of apple cider vinegar for diabetes […]