A dry cough can be incredibly irritating—even if it’s not always serious. The good news? The treatment of dry cough has become simpler with the availability of both medications and effective home remedies. This type of cough is typically non-productive, meaning it doesn’t bring up mucus, and is often accompanied by a scratchy or tickling sensation in the throat.
In this article, we’ll explore the causes, diagnosis, and most importantly, the most effective ways to treat a dry cough—naturally and medically.
Dry Cough
A dry cough is a non-productive cough that doesn’t produce phlegm or mucus. It is a reflex action that helps clear the airways of irritants and foreign particles. Unlike a productive cough, which helps clear mucus, a dry cough tends to linger and can become chronic if not treated properly.
Causes of Dry Cough
We’ve divided the causes into two main categories:
Most Common Causes of Dry Cough
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Acid reflux can irritate the throat, triggering a chronic dry cough. Symptoms of GERD are Heartburn, sour taste, and burning chest sensation. The possible treatments could be Antacids, dietary adjustments, and lifestyle changes.
- Respiratory Tract Infections (RTIs): Includes common cold, acute bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis (TB), or pertussis (whooping cough).
- Post-Infectious Cough: This dry cough may persist even after the primary infection has cleared. It usually lasts a few days to a few weeks.
- Asthma: A leading cause of chronic cough in both children and adults. Often presents with wheezing, shortness of breath, and a tight feeling in the chest. The possible treatment of asthma is inhaling corticosteroids or bronchodilators.
RELATED POST: 8 Common Allergic Foods You Should Avoid [Might Causing You Allergy]
Less Common Causes of Dry Cough
- Environmental Irritants: Smoke, pollution, dust, or dry air can trigger coughing, especially in sensitive individuals.
- ACE Inhibitors: Common blood pressure medications (e.g., lisinopril) can cause a persistent dry cough in up to 35% of patients.
- Foreign Body Aspiration: Sudden onset of coughing during eating may indicate choking or obstruction.
- Whooping Cough (Pertussis): A bacterial infection that leads to intense, dry, whooping-style coughing fits.
- Psychogenic Cough: Often called a “habit cough,” it usually occurs in children and can persist without any underlying illness.
- Chronic Lung Diseases: Conditions like interstitial lung disease, sarcoidosis, bronchiectasis, or cystic fibrosis can also present with a dry cough.
How Is Dry Cough Diagnosed?
Your doctor may perform several evaluations based on your symptoms:
- Chest X-ray – to check for infections or lung issues
- Spirometry – a lung function test
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) – to evaluate breathing capacity
- Allergy Testing – to rule out environmental or food allergens
Once the cause is identified, the right treatment for a dry cough can be initiated.
What Are the Treatments for Dry Cough?
1. Medications
- Cough Suppressants (Antitussives): Best for short-term relief. Look for dextromethorphan-based syrups.
- Lozenges: Often contain soothing agents like menthol or antibacterial compounds to reduce throat irritation.
- Linctus or Cough Syrups: These soothe the throat lining and reduce the urge to cough.
- Antihistamines: Especially useful if allergies are the cause. First-generation antihistamines may also help improve sleep.
Important: Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting new medications—even OTC ones.
2. Home Remedies
- Honey + Warm Water + Lemon: A natural cough suppressant. Take 1–2 teaspoons before bed (safe for children over 12 months only).
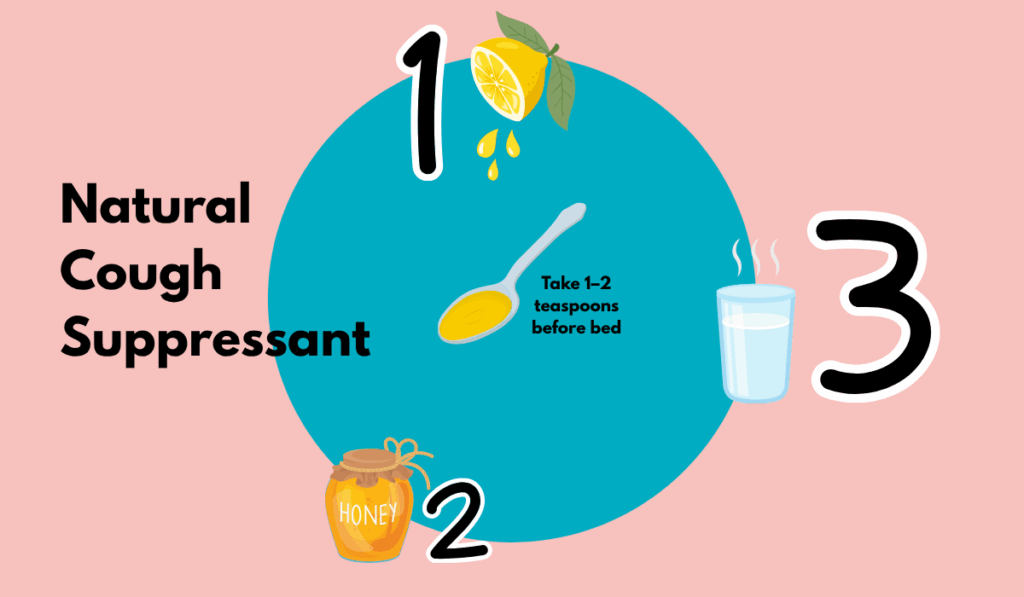
- Warm Liquids: Herbal teas and warm broths can soothe throat inflammation.
- Saltwater Gargle: Mix 1/2 tsp salt in warm water and gargle twice daily to reduce irritation.
3. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Avoid smoking or secondhand smoke
- Stay hydrated—drink at least 8–10 glasses of water daily
- Use a humidifier to moisten dry indoor air
- Limit exposure to allergens and dust
- Allergy-proof your bedroom using mattress covers and air purifiers
Potential Complications of Untreated Dry Cough
If left untreated, a persistent dry cough may cause:
- Insomnia
- Fainting or headaches
- Incontinence (especially in women)
- Vomiting or sore abdominal muscles
- Subconjunctival hemorrhage (red eyes)
When to See a Doctor?
Seek medical advice if:
- The cough lasts longer than 10 days
- You experience shortness of breath or chest pain
- You notice blood in the mucus
- You have underlying conditions like asthma or GERD
- The cough worsens at night
- Your child under 6 months develops a persistent cough
- You develop a high fever or hoarseness
Final Words
While a dry cough can be a minor annoyance, it’s essential not to ignore persistent symptoms. With proper diagnosis and treatment—either medical or natural—relief is achievable. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment of dry cough based on your symptoms and medical history.
